Blockchain
What are Central Bank Digital Currencies?
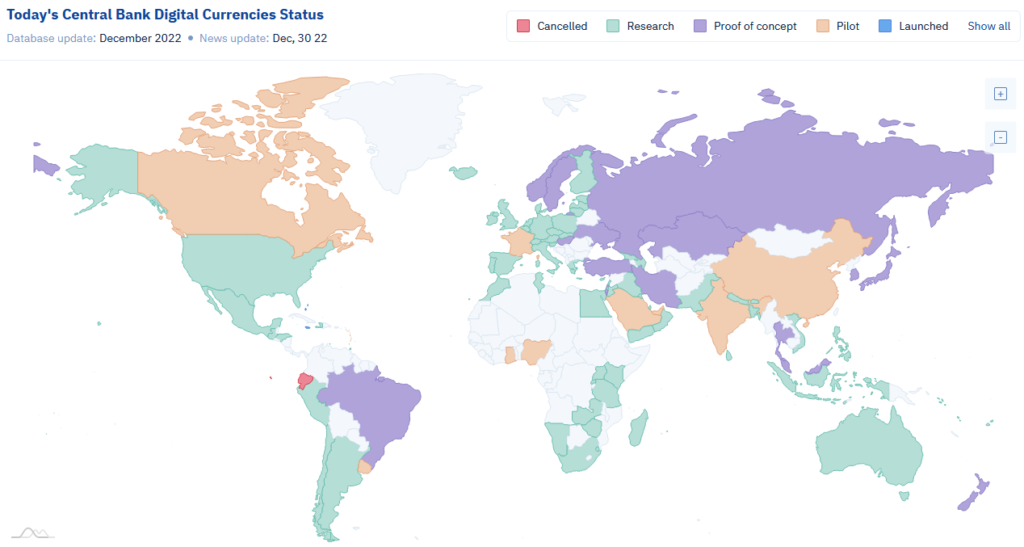
Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) are digital versions of a country’s fiat currency, issued and backed by the central bank. While many central banks around the world are exploring the potential use of CBDCs, only a few countries have actually launched pilot programs or full-scale implementations of CBDCs.
One of the first countries to launch a CBDC is the People’s Republic of China. In October 2020, the People’s Bank of China (PBOC) launched a pilot program for its digital currency, the Digital Currency Electronic Payment (DCEP), in four cities: Suzhou, Chengdu, Shenzhen, and Chengdu. The DCEP is designed to function like physical cash and can be used for P2P transactions, but it can also be transferred and stored electronically. The PBOC has stated that the goal of the DCEP is to improve the efficiency of the financial system, increase financial inclusion, and reduce the risk of financial crime.
Another country that has launched a CBDC is the Bahamas. In October 2020, the Central Bank of the Bahamas launched the Sand Dollar, a digital version of the Bahamian dollar that can be used for P2P transactions. The Sand Dollar is designed to increase financial inclusion and improve the efficiency of financial transactions in the Bahamas, particularly in the remote islands where access to traditional financial services is limited.
Other countries that are currently exploring or piloting CBDCs include Sweden, the European Union, the United States and lately Egypt. The Swedish central bank, the Riksbank, has been studying the potential use of a CBDC, known as the e-krona, since 2017. In 2020, the Riksbank announced that it was launching a pilot program to test the technical feasibility of the e-krona. The European Central Bank is also exploring the potential use of a CBDC, known as the digital euro, and is currently conducting a public consultation on the topic. In the United States, the Federal Reserve has also expressed interest in the potential use of a CBDC and has launched a research program to study the topic.
One risk of CBDCs is the potential for reduced demand for commercial bank deposits. If individuals and businesses start holding CBDCs instead of traditional bank deposits, this could lead to a decrease in the demand for commercial bank deposits, which could in turn reduce the profitability of banks and impact their ability to lend. This could have negative consequences for the stability of the financial system and the economy as a whole.
Another risk of CBDCs is the potential for their use in illicit activities, such as money laundering and financing terrorism. CBDCs, like any other digital currency, can be transferred and stored electronically, making it easier for individuals to engage in such activities without being detected. It is important for central banks and regulatory authorities to put in place appropriate safeguards to prevent the use of CBDCs for illicit purposes.
A third risk of CBDCs is the potential for cybersecurity attacks. As CBDCs are digital currencies, they are vulnerable to cyber attacks, which could compromise the security and integrity of the financial system. It is important for central banks to have robust cybersecurity measures in place to protect against such attacks.
Overall, while CBDCs are still in the early stages of development and adoption, they have the potential to bring numerous benefits, such as increasing financial inclusion and improving the efficiency of the financial system. It is likely that more countries will join the list of those using CBDCs in the future as central banks continue to explore the potential benefits and challenges of these digital currencies.
Blockchain
Fireblocks buys Australian blockchain start-up BlockFold

Fireblocks, the crypto company backed by Sequoia Capital and Coatue Management, has acquired BlockFold, a Melbourne-based start-up that helps financial institutions build blockchain-based systems.
As per Bloomberg , Fireblocks paid about $US10 million ($15.6 million) for BlockFold. While Fireblocks already works with large financial institutions, including Bank of New York Mellon, BNP Paribas and the Tel Aviv Stock Exchange, it has predominantly offered them services around custody technology.
New York-based Fireblocks is one of crypto’s most well-funded start-ups, having raised some $US1.2 billion so far. The company, which employs around 650 people in the US and Israel, was valued at $US8 billion in its latest financing round in January 2022.
The deal comes as large Wall Street firms ramp up efforts to issue and trade traditional financial assets like bonds and private-equity investments over blockchain networks, seeking to simplify processes and cut costs.
Founded in 2021, BlockFold specialises in tokenisation and smart-contract development for clients such as large financial institutions. Fireblocks and BlockFold have already worked together on projects including National Australia Bank’s recent cross-border stablecoin transfer.
Blockchain
Brazil Enhances National Identity Card Security with Blockchain Technology

In a significant stride toward modernization, Brazil is rolling out a novel national identity card system, fortified by the integration of a blockchain network. This innovative approach is set to bolster the security of data sharing between the Federal Revenue Service and civil identification authorities.
The cornerstone of this system is the shared registry known as b-Cadastros, designed to underpin the operations of the revenue service. This comprehensive platform facilitates searches, issuance, and modifications of the new ID cards and tax registration numbers. Notably, the platform’s development was orchestrated by Serpro, Brazil’s state-owned IT services corporation.
Serpro’s President, Alexandre Amorim, emphasized the pivotal role of the b-Cadastros blockchain platform in fortifying the National Identity Card project. “The use of the b-Cadastros blockchain platform is a major differentiator for the security and reliability of the National Identity Card project,” he stated.
The National Civil Identity Card (ICN) represents an upgraded iteration of Brazil’s traditional paper-based ID cards, and the nationwide issuance commenced in July 2022. The overarching goal of this project is to centralize the nation’s civil identification system and harness the ICN database to authenticate individuals accessing online public services.
The modern plastic card boasts an innovative feature: it empowers users to generate a single digital version of their identity document. This advancement enhances security, as it allows for validation through a printed QR code. In adopting blockchain technology for the ID cards, the Brazilian government anticipates streamlining processes and curbing fraud and illegal activities. Presently, individuals can request identification cards in all of Brazil’s 27 states, which presents challenges in terms of data integrity and security.
Serpro’s Amorim elaborated on the significance of blockchain technology in safeguarding personal data and thwarting fraudulent activities, thus delivering a more secure digital experience for Brazilian citizens.
The states of Rio de Janeiro, Goiás, and Paraná are set to pioneer the blockchain-based version of the national revenue service’s shared registry for the issuance of the new ID cards this week. The remaining states are poised to follow suit over the next six weeks, marking a significant step forward in enhancing the security and efficiency of Brazil’s identity verification and taxation systems.
Source: Forbes
Blockchain
Horizen’s $ZEN Holders Take the Helm with the DAO Launch

The Horizen community, get ready to embark on a revolutionary journey in governance as the Horizen DAO steps into the spotlight, as per Horizen’s new announcement.
Horizen, a public, open-source blockchain protocol, boasts a thriving ecosystem composed of developers, miners, node operators, and holders of $ZEN tokens across various blockchain networks. The introduction of the Horizen DAO paves the way for increased community involvement in decision-making and offers a platform for your voices to shape the project’s path.
Discovering the Horizen DAO
DAO, which stands for “Decentralized Autonomous Organization,” has emerged as the gold standard for decentralized governance in the blockchain world and beyond, as per Horizen’s new announcement.
Horizen has always been driven by its community, acknowledging the critical role of a strong social layer in upholding integrity throughout the ecosystem, as stated in Horizen’s new announcement. This ethos is guided by principles such as transparency, accountability, security, community engagement, continuous improvement, and social responsibility. Dive deeper into Horizen’s guiding principles on the Horizen governance page.
Stages of Proposals and Voting
The Horizen DAO takes decentralization of decision-making to new heights, encompassing both technical and non-technical aspects, along with other substantial system enhancements, as outlined in Horizen’s new announcement.
Protocol Improvement Proposals (IPs) are a well-established mechanism for selecting and implementing fresh features and fundamental protocol adjustments in numerous blockchain projects, as per Horizen’s new announcement. In Horizen’s case, these IPs are the cornerstone of the Horizen DAO’s community-driven governance. For Horizen’s primary chain and the EON sidechain, we respectively refer to these as ZenIPs and EONIPs, and they are the lifeblood of our governance process.
Ultimately, it’s the $ZEN token holders who wield the power to steer the future of Horizen, shaping the network’s evolution through active participation in the Horizen DAO, as per Horizen’s new announcement. Any holder of $ZEN can cast their vote on proposed improvements, while those with the requisite amount of $ZEN, either held or delegated, can propose changes to the community. To ensure effective community governance, users will also have the option to delegate their voting authority to individuals they trust as capable stewards of Horizen’s core values.
For a comprehensive understanding of the Horizen DAO, including its proposal phases, voting procedures, Constitution, and more, we invite you to explore the Horizen Governance page. Join us on this exciting journey to help mold the future of Horizen – we’re delighted to have you on board, as announced by Horizen.
-

 Altcoins4 years ago
Altcoins4 years agoProject Review: Pi Network, a New Scam Project in Town
-

 Bitcoin4 years ago
Bitcoin4 years agoBitcoin Worth $1.2M Seized From Arrested Indian Hacker
-

 Altcoins5 years ago
Altcoins5 years agoReview: Play Arcade Games Inside ARK Wallet And Win Some Free Cryptocurrency
-

 Blockchain5 years ago
Blockchain5 years agoA Full Review: Utopia A New Decentralized P2P Blockchain
-

 Bitcoin5 years ago
Bitcoin5 years agoAnother Exit Scam: NovaChain Shuts Down
-

 Exchanges5 years ago
Exchanges5 years agoCrex24 Will Require KYC Verification
-

 Bitcoin5 years ago
Bitcoin5 years agoJohn McAfee Has Gone Missing
-

 Altcoins5 years ago
Altcoins5 years agoElrond Partners With ChainLink










